Thyroid Disease and Pregnancy
Medical Problems
Obie Editorial Team
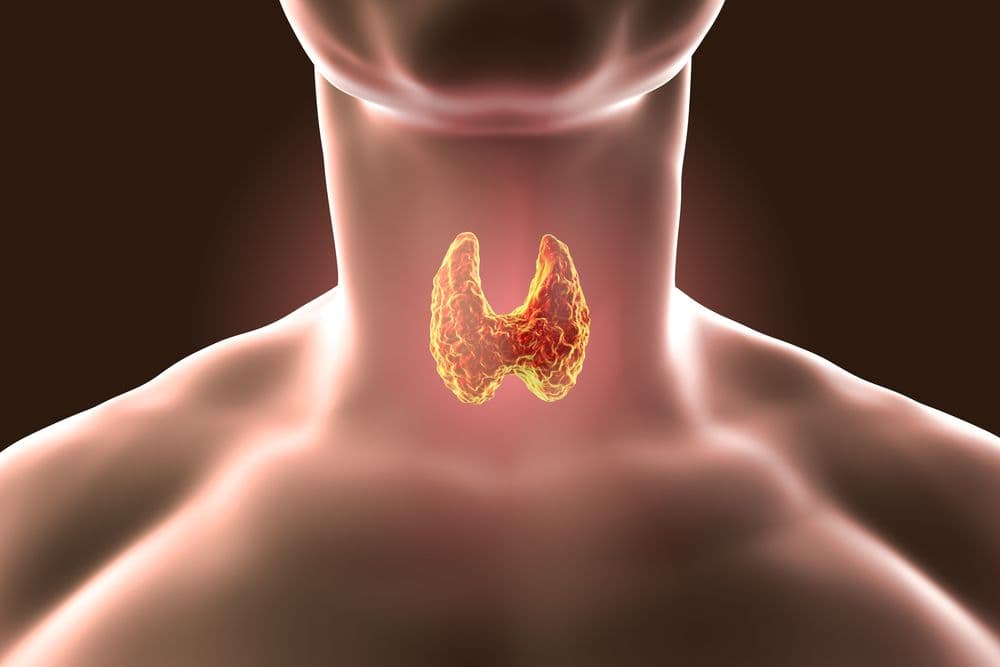
The thyroid sits near the front of your neck, just beneath your larynx or "voice box". Part of the dynamic endocrine gland system, your thyroid produces essential hormones that help regulate your body's functions, making sure everything runs smoothly.
The thyroid gland is responsible for creating thyroid hormones, which skillfully oversee the rate at which your body conducts its critical activities. It's in good company with other hardworking endocrine glands, like the pancreas, pituitary, adrenal glands, parathyroid glands, testes, and ovaries. Each plays a unique role in maintaining your body's harmony.
Thyroid issues are common, especially when you're on the exciting journey of trying to conceive or during pregnancy, affecting millions across America. It's important to know that an underactive thyroid may elevate your risk of miscarriage, so let's get proactive about your thyroid health!
How are thyroid diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosing thyroid disease starts with a thorough history and physical examination to get the complete picture. However, real clarity comes from lab tests, most notably the TSH test. Many symptoms of thyroid disease—like fatigue, weight fluctuations, and intolerance to temperature changes—may also appear in individuals without thyroid disease. This makes testing a crucial part of getting accurate insights into your thyroid health.
What happens during a thyroid disease examination?
- Feeling the neck for any abnormalities
- Listening to the thyroid gland with a stethoscope
- Testing reflexes
- Checking blood pressure, heart rate, and rhythm
- Measuring height and weight, and calculating Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Assessing the face, eyes, nose, skin, nails, and hands for any signs
Clinical signs of thyroid disease
- Over/underweight
- Intolerance to cold
- Intolerance to warmth
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism:
| Hypothyroid | Hyperthyroid |
|
|
Thyroid disease tests
- TSH - Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- Anti-thyroid Microsomal Antibody Testing
- Total T4/ Total Thyroxine
- Free T4 / Free Thyroxine
- Total T3 / Total Triiodothyronine
- Free T3 / Free Triiodothyronine
- Thyroglobulin/Thyroid Binding Globulin/TBG
- T3 Resin Uptake (T3RU)
- Reverse T3
- Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb) / Antithyroid Peroxidase Antibodies
- Antithyroid Microsomal Antibodies / Antimicrosomal Antibodies
- Thyroglobulin Antibodies / Antithyroglobulin Antibodies
- Thyroid Receptor Antibodies (TRAb)
- Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulins (TSI)
Imaging tests
- MRI or CT Scan
- Thyroid Ultrasound
- Nuclear Scan/Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAI-U)
What are the different types of thyroid diseases?
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive gland producing excess thyroid hormone
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive gland with insufficient hormone production
- Hashimoto’s Disease: An autoimmune condition leading to hypothyroidism
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder causing hyperthyroidism
- Goiter
- Nodules
- Thyroid Cancer
An enlarged thyroid gland is often referred to as a "goiter," and inflammation can lead to its enlargement. Bringing your thyroid function into balance before and during pregnancy is incredibly beneficial, as it affects your fertility and the health of your developing baby. Taking action early can increase your opportunity for a healthy pregnancy outcome and a healthy baby.
Hypothyroidism and fertility
Are your menstrual cycles irregular? Do conception challenges persist? Hypothyroidism could be the underlying cause. During pregnancy, untreated hypothyroidism increases miscarriage risk and can affect your baby's development. On the bright side, hypothyroidism is manageable! Regularly, about one in ten women may face this condition during pregnancy, many of whom are unaware. Its symptoms can blend into the general tiredness experienced during pregnancy, making it crucial to address early on.
Here are the classic symptoms of hypothyroidism:
- Lethargy, fatigue, and weakness
- Weight gain or increased difficulty losing weight
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Depression
- Decreased libido
- Reduced heart rate
- Development of goiter
The impacts of hypothyroidism during pregnancy might include more subtle changes, such as gradual weight gain, changes in skin condition, and menstrual irregularities. Given these subtle signs, testing for thyroid function in pregnancy should be routine practice to avoid unforeseen complications.
Untreated hypothyroidism can result in infants with lowered IQ. Proactive testing and treatment can lessen these risks. Causes of hypothyroidism can vary—from autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto's disease, to post-infection inflammation, or even partial or total removal of the thyroid.
Treatment is effective and straightforward: daily synthetic thyroid hormone. Within approximately eight weeks, your thyroid hormone levels will begin to normalize, paving the way for a healthier pregnancy journey. It's quite common for women previously treated for hypothyroidism to adjust dosages during pregnancy to maintain balance. Rest assured, with the right dose, both you and your baby will thrive.
Read More








_0.jpg&w=3840&q=75&dpl=dpl_FDQpuTuQR2MXtaiuWZjLv4GSXnKU)
